| Process Instrumentation | Flow Measurement |
Coriolis Mass Flow Meter is widely used flow meter in process industry for its versatility and ability to directly give mass flow rate.

Working Principle
Coriolis flow meter uses the principle of Coriolis Effect. When a tube is vibrating laterally and fluid is passed through it, it starts to distort due to weight and flow of fluid.
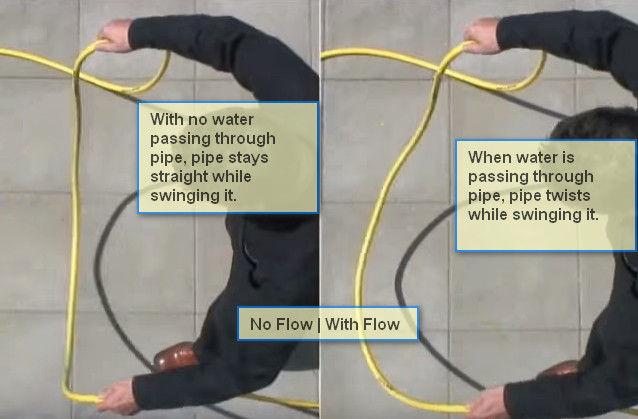
This distortion can be measured and mass flow can be inferred directly from it, including density of the fluid.
[google-square-ad]
- Most common configuration includes one or two U-shaped flow tube with inlet on one side and outlet on the other enclosed in a sensor housing connected to an electronics unit.
- The flow is guided into the U-shaped tube.
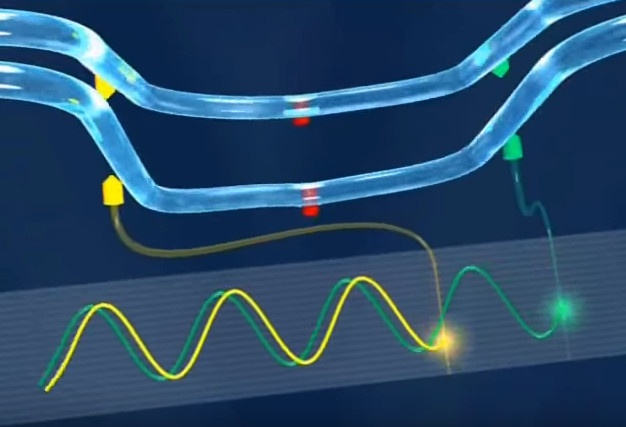
- When an oscillating excitation force is applied to the tube causing it to vibrate, the fluid flowing through the tube will induce a rotation or twist to the tube because of the Coriolis acceleration acting in opposite directions on either side of the applied force.
- Vibration of Coriolis flowmeters has very small amplitude, usually less than 2.5 mm (0.1 in), and the frequency is near the natural frequency of the device, usually around 80 Hz.
- Finally, the vibration is commonly introduced by electric coils and measured by magnetic sensors.
- This twist results in a phase difference (time lag) between the inlet side and the outlet side and this phase difference is directly affected by the mass passing through the tube.
[google-square-ad]
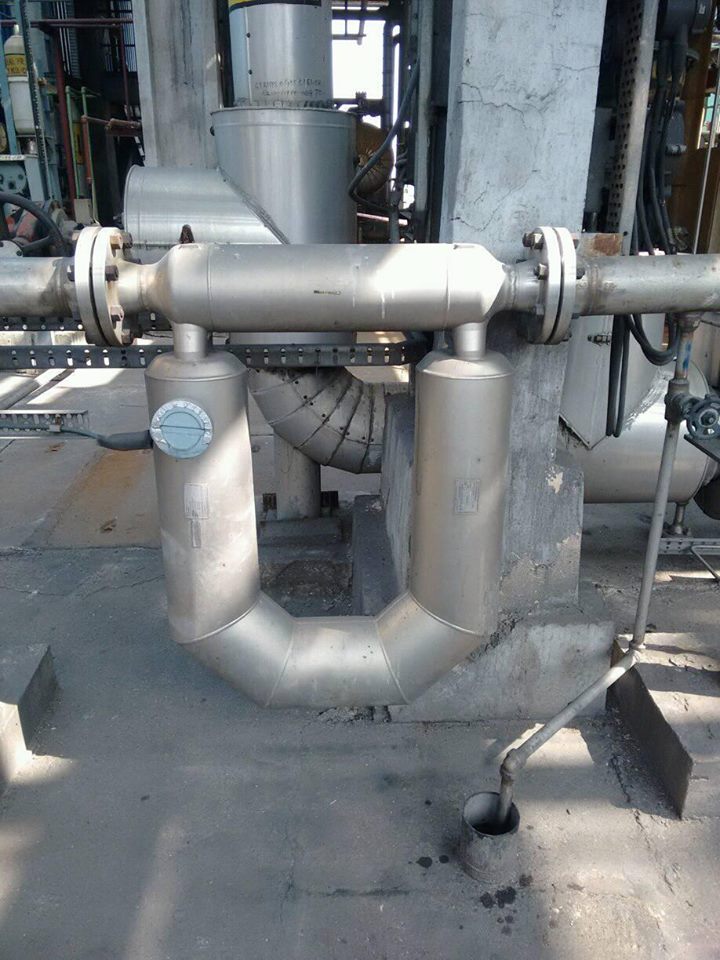
Installation of Coriolis Flow Meter
Following photo shows a typical installation of a Coriolis Mass Flow Meter.

- There are no Reynolds number limitations associated with Coriolis mass flow meters. They are also insensitive to velocity profile distortion and swirl. Therefore, there is no requirement for straight runs of relaxation piping upstream or downstream of the meter to condition the flow.
- The flow meter should be installed so that it will remain full of liquid and so air cannot get trapped inside the tubes.
- In sanitary installations, the meter must also drain completely.
- The most desirable installation is in vertical upward flow pipes, but installations in horizontal lines are also acceptable.
- Installations where the flow is downward in a vertical pipe are not recommended.
- In newer Coriolis designs, normal pipe vibration should not affect the performance of the Coriolis meter if it is properly supported by the process piping.
- No special supports or pads are needed for the flow tube, but standard piping supports should be located on either side of the meter.
- If the installation instructions require special hardware or supports, the particular meter design is likely to be sensitive to vibration, and the pulsation dampeners, flexible connectors, and mounting/clamping attachments recommended by the manufacturer should be carefully installed.
[google-square-ad]
Advantages
- Coriolis meter can be very accurate irrespective of the type of gas or liquid that is being measured.
- Because mass flow is measured, the measurement is not affected by fluid density changes.
- Same measurement tube can be used for hydrogen gas and bitumen without recalibration.
- They can be used for the measurement of natural gas flow.
- Recently, single straight tube designs are available to measure some dirty and/or abrasive liquids that may clog the older U-shaped design.
- Coriolis flow meter measures the mass flow rate directly which eliminates the need to compensate for changing temperature, viscosity, and pressure conditions.
- In addition, the relative insensitivity to density allows Coriolis mass flowmeters to be applied in applications where the physical properties of the fluid are not well known.

Disadvantages
- Be particularly careful when using Coriolis mass flowmeters to measure gas/vapor flows because flow rates tend to be low in the flow range (where accuracy is degraded).
- Also, in gas/vapor applications, large pressure drops across the flowmeter and its associated piping can occur.
Applications
- Coriolis mass flowmeters measure the mass flow of liquids, such as water, acids, caustic, chemicals, and gases/vapors.
- This flowmeter can be applied to sanitary, cryogenic, relatively clean, and corrosive liquids and gases/vapors in pipes smaller than 6-12 inches.
- General applications are found in the water, wastewater, mining, mineral processing, power, pulp and paper, petroleum, chemical, and petrochemical industries.
- Straight-tube designs are available to measure some dirty and/or abrasive liquids.
- Many applications for Coriolis mass flowmeters are found in chemical processes where fluids can be corrosive and otherwise difficult to measure.
- These flowmeters can also be used in chemical feed systems found in most industries.
- The industries in order of higher to lower are chemical, oil and gas, food and beverage, pharmaceutical, pulp and paper, power, metals and mining, and water and wastewater followed by all others in small amounts.
[google-square-ad]
Materials of Construction
Materials of construction are generally limited to stainless steel and Hastelloy C.
Videos from youtube
Siemens FC430 Coriolis Meter – How it Works
Coriolis Flow Meter
| Process Instrumentation | Flow Measurement |
