It is essential to achieve highest quality of weld such that weld is as good as parent metal. Problems in welds can be classified as :
- Imperfection: Any deviation from the ideal weld.
- Defect: An unacceptable imperfection.
Classification of imperfections according to BS EN ISO 6520-1:
This standard classifies the geometric imperfections in the case of fusion welding, dividing them into six groups:
- Cracks
- Cavities
- Solid inclusions
- Lack of fusion and penetration
- Imperfect shape and dimension
- Miscellaneous imperfections
It is important that an imperfection is correctly identified thus allowing for the cause to be identified and actions taken to prevent further occurrence.
Cracks
Definition: An imperfection produced by a local rupture in the solid state, which may arise from the effect of cooling or stresses. Cracks are more significant than other types of imperfection, as their geometry produces a very large stress concentration at the crack tip, making them more likely to cause fracture.
Types of crack:
- Longitudinal
- Transverse
- Radiating (cracks radiating from a common point)
- Crater
- Branching(a group of connected cracks originating from a common crack)
These cracks can be situated in the:
- Weld metal
- HAZ
- Parent metal
Exception: Crater cracks are found only in the weld metal.
Depending on their nature, these cracks can be:
- Hot cracks (i.e. solidification cracks and liquation cracks).
- Precipitation induced cracks (ie reheat cracks, present in creep resisting steels)
- Cold cracks (i.e. hydrogen induced cracks).
- Lamellar tearing
Cavities
Cavities can be of various types as follows :
Gas Cavity : Formed by entrapped gas.
- Gas Pore
- Uniformly distributed porosity.
- Clustered (Localised Porosity).
- Linear porosity.
- Elongated Cavity.
- Worm-hole.
- Surface pore.
Shrinkage Cavity : Caused by shrinkage during solidification.
- Interdendritic Shrinkage.
- Crater pipe.
- Interdendritic micro-shrinkage
- Transgranular micro-shrinkage.
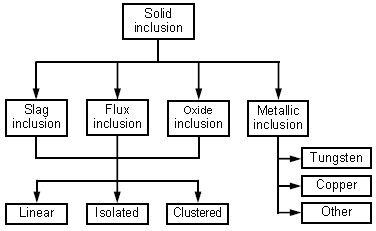
Solid Inclusions
- Slag Inclusion
- Flux Inclusion
- Oxide Inclusion
- Metallic Inclusion
Lack of fusion and penetration
Lack of fusion
Definition: Lack of union between the weld metal and the parent metal or between the successive layers of weld metal.
- Lack of side wall fusion.
- Lack of inter-run fusion.
- Lack of root fusion.
Lack of Penetration
- Incomplete penetration.
- Incomplete root penetration.
Imperfect Shape and Dimensions
- Undercut.
- Excess weld metal.
- Excess penetration.
- Overlap.
- Linear misalignment.
- Angular distortion.
- Incompletely filled groove.
- Irregular width.
- Root concavity.
- Burn through.
Miscellaneous Imperfections
- Stray arc.
- Spatter.
- Torn surface.
- Grinding mark.
- Chipping mark.
- Underflushing.
- Misalignment of opposite runs.
- Temper color.
